1.0 Introduction: Navigating a Market of Complexity and Contradiction
The South Korean housing market presents a dynamic and often contradictory landscape for analysis. It is an environment shaped by decades of intense government intervention, a unique set of consumer preferences that diverge sharply from global norms, and significant supply-side constraints that persistently challenge policy objectives. For investors, developers, and policymakers alike, a strategic understanding of these deeply interconnected forces is not merely beneficial—it is essential for navigating the market’s inherent complexities.
This report provides a data-driven analysis of the market’s current state and near-term trajectory. Its core objective is to deconstruct the key factors at play by examining macroeconomic drivers, historical and current price dynamics, deep-rooted supply and demand fundamentals, and the outsized role of the Seoul metropolitan area. Furthermore, it will investigate the overarching impact of the nation’s dense regulatory framework and public procurement systems, which together form a critical, yet often overlooked, institutional layer influencing market outcomes.
To achieve this, the report is structured to guide the reader through a logical progression of analysis. We will begin by establishing the macroeconomic and social context that underpins housing demand. This is followed by a detailed examination of price trends and affordability. Subsequently, the report will dissect the structural constraints and alarming trends within the housing supply chain, before concluding with an analysis of the institutional landscape and a strategic outlook on potential pathways toward market normalization.
2.0 Macroeconomic and Social Context: The Foundations of Housing Demand
A robust analysis of any housing market must begin with its foundational economic and social drivers. These elements create the fundamental pressures that shape consumer behavior, purchasing power, and overall demand. This section evaluates South Korea’s near-term economic trajectory, key demographic shifts, and the unique consumer psychology that collectively establish a resilient and persistent demand for housing, particularly in urban centers.
2.1 Economic Outlook and Market Sentiment
According to the “Economic Cycle Clock” published by Statistics Korea, the national economy is transitioning into a more favorable phase. After passing through a recovery phase in 2024, key economic indicators are projected to enter an upward trend in 2025. This forward-looking trajectory suggests a strengthening economic environment.
Of particular importance to the housing sector is the forecast for Construction Investment, which is expected to recover and enter an expansionary phase by June 2025. This anticipated shift from recovery to expansion creates a firm macroeconomic tailwind for the housing sector, signaling that any near-term market weakness is more likely attributable to structural supply issues than a lack of economic support.
2.2 Core Demand Drivers: Demographics and Liquidity
Several fundamental factors are exerting sustained upward pressure on housing demand in South Korea. These drivers, largely independent of short-term policy shifts, create a baseline of demand that consistently tests the market’s supply capacity.
- Household Growth: The absolute number of households continues to expand, fueling organic demand for housing units. This growth is driven by a confluence of factors, including a recent increase in marriage rates, the structural trend toward single-person households, and a steadily expanding foreign resident population.
- Financial Liquidity: The financial environment is becoming increasingly supportive of housing purchases. A significant increase in the M2 money supply indicates greater liquidity in the economy. This is compounded by market expectations of a downward trend in interest rates, which would lower borrowing costs and further stimulate demand for mortgages and property investment.
The persistence of these demand-side factors creates a challenging environment for policymakers, especially when juxtaposed with the significant supply-side constraints and contractions that will be detailed later in this report.
2.3 Consumer Psychology: The Unwavering Demand for Homeownership
The South Korean housing consumer exhibits a unique set of priorities and a cultural disposition that strongly favors homeownership, ensuring a resilient baseline of market demand. Analysis of a 2025 IPSOS global survey reveals several key characteristics that distinguish the Korean market.
First, concerns over housing costs are exceptionally high. A comparison of South Korea’s top housing challenges against the 30-country global average highlights a significant gap in public anxiety over affordability.
| Housing Challenge | South Korea | Global Average (30 Countries) |
| High property prices | 68% | 51% |
| Cost of renting | 55% | 33% |
Second, housing preferences in South Korea are uniquely concentrated on urban apartments. While the global preference leans toward detached homes in suburban or rural areas, 55% of South Koreans prefer an “Inner-city apartment.” This is a stark contrast to preferences in countries like the United States, Germany, or Japan, where suburban detached homes are the dominant choice.
Third, the cultural and psychological importance of owning a home is a powerful market force. Survey data reveals that 80% of South Koreans desire to own their home, and a remarkable 62% report feeling unstable without homeownership. This deep-seated cultural preference is not merely an aspiration but a perceived prerequisite for social and financial stability, ensuring a consistent and resilient demand for property, especially for the highly preferred apartment type in major urban centers. These powerful demand-side drivers are a primary contributor to the price and affordability challenges facing the nation.
3.0 Housing Price Dynamics and Affordability Analysis
Housing prices are the central point of public and political discourse in South Korea, directly impacting household wealth, social equity, and economic stability. This section deconstructs the market’s long-term price trends to reveal the limitations of policy intervention, analyzes the unique market forces that define Seoul as a “superstar city,” benchmarks national prices against international peers, and assesses the severe affordability crisis currently facing the average household.
3.1 Historical Price Cycles and the Limits of Intervention
An analysis of real estate price changes across the past eight government administrations reveals a crucial insight: price appreciation is not solely determined by the direction of government policy. The market has consistently demonstrated an ability to generate upward price pressure irrespective of whether regulatory regimes were being tightened or eased.
For example, the Roh Moo-hyun administration implemented strong regulatory tightening, yet housing prices saw significant growth. Conversely, the subsequent Lee Myung-bak administration pursued broad regulatory easing, and prices continued to climb after an initial period of stabilization. This historical pattern suggests that while government policies have a definite impact, they are often secondary to more powerful underlying factors such as fundamental supply-demand imbalances, liquidity, and speculative pressures that have consistently driven the market cycle.
3.2 The “Superstar City” Effect: Seoul’s Market Dominance
Seoul’s housing market cannot be understood through a national lens alone; it operates under the principles of a “superstar city.” This economic concept describes how global hubs that concentrate top-tier talent, capital, and high-value industries create immense, localized economic value. This concentration has a direct and profound impact on the city’s housing market.
The intense clustering of high-value jobs and capital in Seoul fuels soaring demand for a geographically limited housing stock, inevitably driving up land and property prices. This pressure is compounded by an inelastic housing supply, hemmed in by both natural geography and explicit regulatory constraints, such as the protected green belts surrounding the city. The result is a self-reinforcing cycle of price escalation and market polarization, with a disproportionate focus on high-cost apartments in prime locations, creating a market that behaves fundamentally differently from the rest of the country.
3.3 International Benchmarking: A Nuanced Price Perspective
When viewed from a national, aggregate perspective, South Korea’s recent house price growth appears relatively stable compared to many of its OECD peers. This nuanced view challenges the narrative of a uniformly runaway market.
- Over the last five years, South Korea’s nominal house price increase of 5.6% is modest when benchmarked against other major economies. For example, the United States saw a 54.9% increase, while Germany experienced a 12.7% rise over the same period.
- The rent-to-price ratio index, a key indicator of market balance, has also remained stable in South Korea, changing by only -0.9% over five years.
However, this national stability masks a critical reality: the data is heavily skewed by the “superstar city” effect. While national averages appear contained, the price pressure and affordability challenges within Seoul are acute and far exceed the national trend. The Korean housing market is best understood as two distinct markets: Seoul and the rest of the nation.
3.4 Current Affordability Crisis
The price dynamics within Seoul have culminated in a severe affordability crisis for the median household. Key metrics from 2024 paint a stark picture of this challenge, particularly for the preferred apartment housing type. The Housing Affordability Index (HAI) measures whether a median-income household can afford a median-priced home, with a value below 100 indicating unaffordability. The Price-to-Income Ratio (PIR) measures the number of years of median income required to purchase a median-priced home.
| 2024 Affordability Metrics | Housing Affordability Index (HAI) | Price-to-Income Ratio (PIR) |
| National Average | 84.1 | 7.6 years |
| Seoul Capital Area | 85.6 | 9.3 years |
| Seoul (Apartments) | 64.5 | 10.5 years |
The data is unequivocal. The national HAI of 84.1 already signals an affordability challenge, but the situation in Seoul is critical, with an HAI of just 64.5 for apartments. This means a typical median-income household cannot qualify for a loan to purchase a median-priced apartment in the capital. Furthermore, the PIR of 10.5 for Seoul underscores the immense financial burden, requiring over a decade of the average household’s entire income to purchase a home. This acute affordability crisis is a direct consequence of the supply-side failures detailed in the following section.
4.0 The Housing Supply Chain: Structure, Constraints, and Imbalances
To understand the South Korean housing market’s structural problems, it is crucial to analyze the supply side. A series of deep-seated constraints, institutional frameworks, and recent market shocks have led to a significant contraction in new housing, particularly in the affordable sector. This section dissects the country’s dual-track development framework, analyzes alarming trends in both the apartment and non-apartment sectors, and deconstructs the official housing supply rate to reveal a more accurate picture of market tightness.
4.1 The Dual Framework of Housing Development
Housing construction in South Korea is governed by a two-track legal system that creates a fundamental bifurcation in the market. The specific framework applied depends largely on the scale of the project.
- The Housing Act (주택법): This act governs large-scale developments of 30 units or more. It is the primary framework for the pre-sale apartment complexes that dominate the market and public consciousness. These projects follow a complex, regulated process from land acquisition to pre-sales and final construction.
- The Building Act (건축법): This framework is applied to smaller projects of less than 30 units. This category includes vital housing types such as villas, multi-family homes, and officetels, which traditionally serve as a source of more affordable rental and for-sale housing.
The critical implication of this dual system is that apartment and non-apartment developments follow vastly different financing, approval, and construction processes. This has led to distinct market behaviors and vulnerabilities, with the non-apartment sector proving far more susceptible to recent economic headwinds.
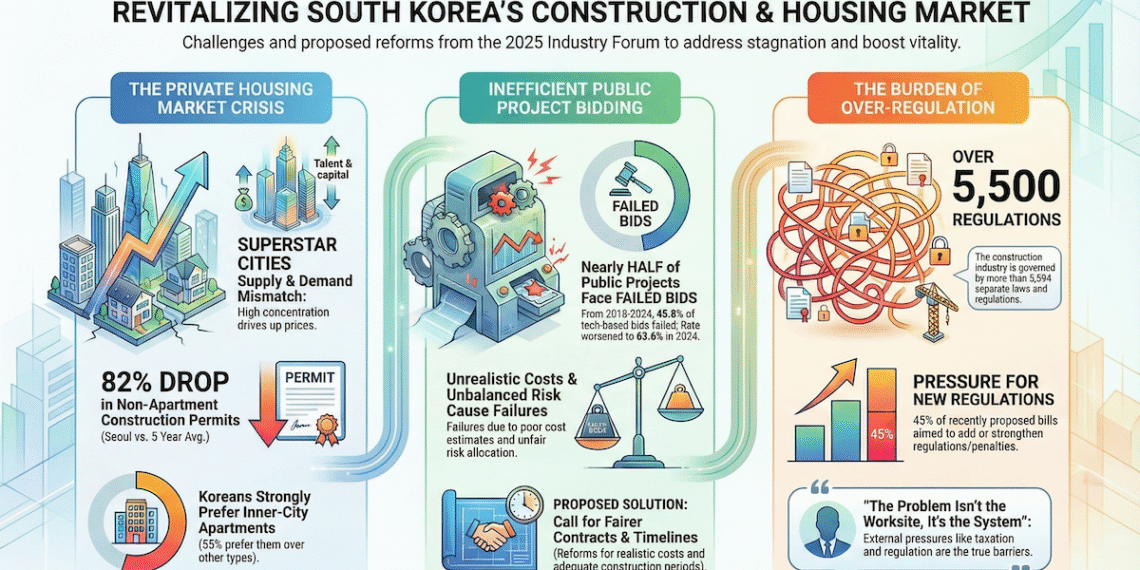
4.2 Alarming Contraction in Housing Supply
Recent data from Seoul reveals a severe downturn in the housing supply pipeline, with both construction permits and starts falling dramatically. The decline is particularly catastrophic in the non-apartment sector, threatening the availability of affordable housing.
In Seoul, private sector housing starts in 2024 are down 54% compared to the trailing five-year average, signaling a near-term supply cliff.
| Private Sector Supply in Seoul (2024 vs. 5-Year Average) | 5-Year Average (’19-’23) | 2024 (Annualized) | % Change |
| Permits (인허가) | 53.5 thousand units | 33.1 thousand units | -38% |
| Starts (착공) | 55.0 thousand units | 25.3 thousand units | -54% |
Drilling down further, the collapse of the non-apartment sector—comprising the villas and multi-family homes that form the backbone of affordable housing for renters and first-time buyers—is even more pronounced. In 2024, permits for non-apartment housing in Seoul have plummeted by 82%, and starts have fallen by 80% compared to the five-year average.
This collapse disproportionately impacts the supply of housing for lower-income households, young people, and renters who rely on this segment of the market. This threatens to create a permanent barrier for a generation of aspiring homeowners, whose deep-seated cultural desire for stability through ownership is being directly thwarted by a failure in the supply of attainable housing.
4.3 Deconstructing the Housing Supply Rate (주택보급률)
The official housing supply rate (주택보급률), a key government metric, can be misleading if not properly contextualized. The headline 2023 figure for the nation is 102.5%, while for Seoul it is a much lower 93.6%. While the national figure suggests a surplus, it fails to capture the full picture of market dynamics.
A more critical evaluation that adjusts for residential-use officetels, vacant homes, and the housing needs of foreign households reveals a lower effective national supply rate of approximately 101%.
More importantly, regional disparities are immense. Maps of the housing supply rate show that Seoul and the surrounding Gyeonggi province have some of the lowest rates in the country. Simultaneously, these are the areas with the highest concentration of officetels being used as primary residences. This indicates that the official statistics undercount the true demand pressure in the capital region, where the supply of traditional housing units has failed to keep pace with the needs of the population. These supply constraints are not merely a function of market forces; they are significantly worsened by the country’s complex and burdensome institutional environment.
5.0 The Institutional Landscape: Regulation and Public Procurement
Market dynamics are not driven by economic forces alone; they are heavily shaped by the institutional framework of regulation and public processes. In South Korea, two critical institutional factors act as significant drags on housing supply: an immense and growing regulatory burden on private construction and systemic inefficiencies within the public construction procurement system. These factors create delays, increase costs, and ultimately constrain the market’s ability to respond to demand.
5.1 The Weight of Regulation on Private Development
The private construction sector in South Korea operates within one of the most complex regulatory environments in the developed world. This framework acts as a structural impediment to the efficient delivery of new housing.
- Scale of Regulation: The construction process is impacted by a documented 5,594 clauses spread across at least 29 laws. This sheer volume creates a daunting compliance challenge for developers.
- Constant Expansion: The regulatory burden is not static; it is constantly growing. On average, 20 new or strengthened construction-related bills are proposed each month in the National Assembly, adding layers of complexity and uncertainty to the development process.
This regulatory density has direct and measurable economic consequences. For apartment redevelopment projects in the Seoul Capital Area, the tangled web of approvals and mandates has increased average construction timelines by 20-25%. Furthermore, strengthened mandates related to safety, environmental standards, and quality control, while often well-intentioned, consistently drive up project costs. This excessive regulation functions as a primary structural barrier to increasing housing supply in a timely and cost-effective manner.
5.2 Public Construction Procurement and the Bid Failure Crisis
The public sector’s ability to contribute to housing supply is being severely hampered by a crisis in its procurement system. The “Technology-Based Bidding” (기술형 입찰) system, used for major public construction projects, is plagued by an exceptionally high rate of bid failures (유찰), where no qualified contractor submits a bid.
This trend has been worsening, with the bid failure rate reaching 65.4% in 2023 and remaining high at 63.6% in 2024. These failures are not random occurrences but symptoms of systemic flaws in the procurement process. The primary causes include:
- Unrealistic Cost Estimation: Project budgets are often based on outdated data from preliminary feasibility studies, failing to reflect current material and labor costs.
- Insufficient Budgets: The funds allocated for crucial pre-construction work, such as bidding preparation and design, are often inadequate.
- Unbalanced Risk Allocation: Contracts frequently place a disproportionate amount of risk on the contractor, discouraging participation.
- Excessive Regulations: Complex qualification requirements and administrative hurdles further deter potential bidders.
The direct impact of these persistent bid failures is the delay of crucial public infrastructure and housing projects. This not only affects the public component of the housing supply but also drives up eventual project costs, placing a greater burden on taxpayers and further straining the national housing market.
6.0 Strategic Outlook and Pathways to Normalization
The South Korean housing market is at a critical juncture. The analysis presented in this report confirms a market defined by the powerful undercurrents of persistent, culturally ingrained demand, which are colliding with severe supply constraints and an institutional framework that often hinders rather than helps. This final section synthesizes the key challenges facing the sector and outlines the strategic pathways proposed in the source materials for creating a more stable, affordable, and functional market for the future.
6.1 Synthesis of Key Market Headwinds
Distilling the preceding analysis, three critical and interconnected challenges emerge as the primary headwinds impeding the normalization of the South Korean housing market.
- Structural Supply Bottlenecks: The market is facing a multifaceted supply crisis. This is driven by a catastrophic collapse in the construction of non-apartment housing, significant project delays in the private sector, and systemic failures in the public procurement system that stall public housing initiatives.
- Affordability and Market Polarization: There is a severe and widening affordability gap, particularly in Seoul. This is fueled by the economic forces of a “superstar city” and exacerbated by a supply chain that is failing to deliver a sufficient diversity of affordable housing options for low- and middle-income households.
- Overarching Regulatory Burden: The complex, overlapping, and constantly expanding regulatory system, encompassing over 5,500 clauses, stands as a fundamental barrier to cost-effective and timely housing development. It increases costs, extends project timelines, and creates uncertainty for both private and public developers.
6.2 Proposed Measures for Market Revitalization
Addressing these deep-seated challenges requires a comprehensive strategy that moves beyond short-term interventions. The following measures, drawn from expert proposals, outline a two-pronged approach focused on revitalizing the private sector and reforming the public framework.
A. Revitalizing the Private Housing Supply
To unblock the private development pipeline and encourage the construction of a wider range of housing types, the following actions are proposed:
- Expand Registered Private Rental Housing: Revitalize the system to increase the stock of stable, long-term rental properties.
- Improve Project Financing: Provide relief and support for Project Financing (PF) loans to ease the credit crunch currently stalling many developments.
- Ease Pre-Sale Price Caps: Rationalize regulations on pre-sale prices to better reflect construction costs and improve project viability.
- Support Non-Apartment Construction: Implement targeted support, including tax incentives and financing, to urgently address the collapse in the supply of villas and other affordable housing types.
B. Enhancing Public Sector Efficiency and Regulatory Reform
To ensure the public sector can effectively contribute to supply and to reduce the structural burdens on the entire industry, the following reforms are critical:
- Streamline Public Housing Delivery: Simplify and accelerate the processes for land development and public housing construction led by public corporations like LH.
- Rectify Public Project Costing: Mandate that public project budgets are based on realistic, up-to-date cost estimates—rather than outdated preliminary studies—to directly address and reduce the high rate of bid failures.
- Rationalize Land Use: Review and reform land use regulations to allow for more flexible and efficient development.
- Undertake Comprehensive Regulatory Overhaul: Initiate a systematic review and simplification of the 5,594+ regulations that impede construction, with a goal of reducing redundancy and lowering compliance costs.
The path to normalization is therefore clear: policy must pivot decisively from a long-standing and often futile focus on demand-side suppression to a sustained, strategic commitment to dismantling the structural and regulatory barriers that have choked housing supply for over a decade.