1.0 Introduction: The 2026 Seoul Metropolitan Investment Landscape
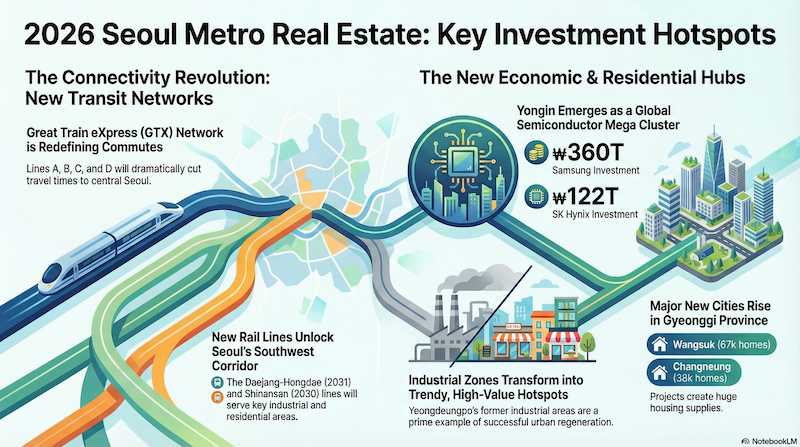
The real estate markets of Seoul and the surrounding Gyeonggi Province are poised for significant transformation in the period leading into 2026. This evolution is driven by a powerful confluence of large-scale urban regeneration projects, major transportation infrastructure expansions, and the strategic development of new economic hubs. This convergence of public policy and private investment is set to reshape land use, enhance connectivity, and unlock substantial value across the metropolitan area. This memorandum provides a comprehensive analysis of these key drivers to identify the most promising investment locations and timelines for discerning investors.
Our analysis will begin with a foundational urban planning shift in Seoul that serves as a catalyst for widespread redevelopment. From there, we will examine the specific high-growth corridors in the Southwest of Seoul, followed by an in-depth look at the rapidly expanding Northern and Southern regions of Gyeonggi Province, each presenting a distinct and compelling investment thesis.
2.0 Foundational Catalyst: Seoul’s 2040 Industrial Area Transformation Plan
A pivotal policy shift is underway that will fundamentally alter Seoul’s urban landscape: the “2040 Seoul Industrial Area Basic Plan.” This strategic initiative represents the first domino in a series of value-unlocking events, designed to revitalize the city’s vast but underutilized industrial zones and transform them from aging manufacturing sites into modern, mixed-use innovation hubs. By promoting high-density, complex development, this plan is set to unlock significant latent land value. Investors can gain a tangible preview of this long-term vision by examining the more immediate “Southwest Corridor Grand Reorganization” plan announced in February 2024, which signals strong political will and foreshadows the principles of the 2040 plan.
The plan’s strategy is twofold, targeting different types of industrial areas with tailored approaches:
- Objective: The plan establishes two primary redevelopment frameworks:
- Industrial Innovation Zones: These zones are intended for large-scale, comprehensive redevelopment, encouraging a mix of commercial, residential, and advanced industrial uses to create new economic centers.
- Industrial Redevelopment Zones: This framework focuses on upgrading existing industrial infrastructure, allowing for modernization and enhancement while preserving the area’s core industrial function.
- Scope: Seoul’s total industrial area spans 19.97 km². This plan specifically targets the 16.76 km² of industrial land that falls outside the four major, pre-existing industrial complexes (which total 3.21 km²).
- Key Timeline: The implementation of this plan has several critical milestones that will serve as market catalysts:
- October 28, 2025: A public hearing will be held for the draft plan.
- November 6, 2025 – January 5, 2026: A public call for “Industrial Innovation Zone” candidate sites will be conducted, with approximately two locations to be selected.
- First Half of 2026: The official “Industrial Area Basic Plan” is scheduled to be announced.
The following table details the distribution of the targeted industrial zones across key districts in Seoul, highlighting the areas with the largest potential for transformation under this new policy.
| District | Semi-industrial Zone (km²) | Industrial Zone (excluding complexes) (km²) |
| Yeongdeungpo-gu | 5.02 | 5.02 |
| Guro-gu | 4.20 | 3.65 |
| Geumcheon-gu | 4.12 | 2.65 |
| Gangseo-gu | 2.92 | 1.81 |
| Seongdong-gu | 2.05 | 2.05 |
| Dobong-gu | 1.49 | 1.49 |
Given that a significant portion of this designated land is concentrated in the Southwest Corridor (서남권), this region presents the most immediate and tangible investment opportunities arising directly from this foundational policy shift.
3.0 Prime Investment Region: Seoul’s Southwest Corridor (서남권)
Seoul’s Southwest Corridor, encompassing districts like Yeongdeungpo, Guro, and Geumcheon, stands as the primary beneficiary where the policy vision of the 2040 Plan becomes a physical manifestation of investment potential. The strategic value of this region is amplified by the powerful convergence of three distinct drivers: the industrial regeneration outlined in the 2040 plan, numerous concurrent public and private redevelopment projects, and transformative infrastructure upgrades. This multi-layered investment thesis creates a robust environment for value appreciation.
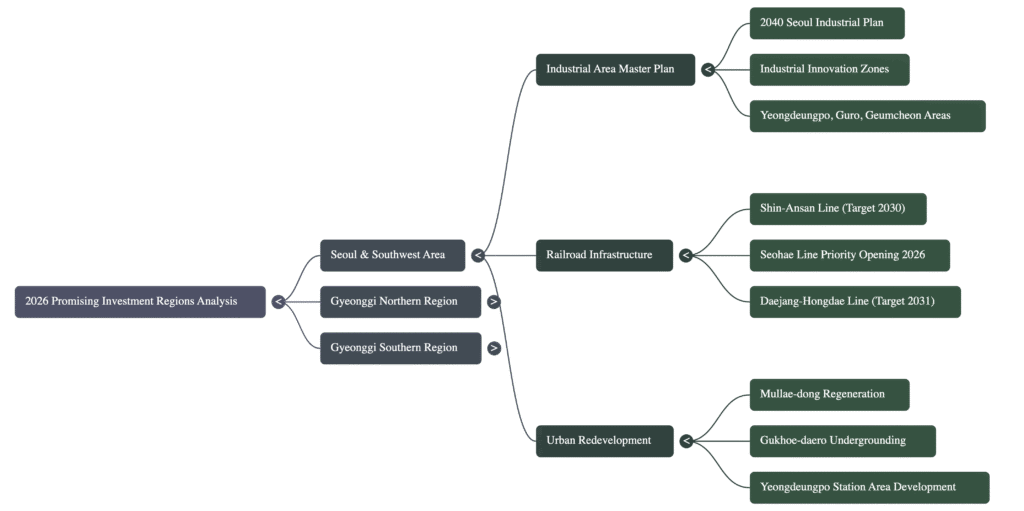
3.1 Yeongdeungpo: Epicenter of Urban Regeneration
Yeongdeungpo is at the heart of this transformation, with its investment potential anchored by the dynamic evolution of Mullae-dong (문래동). Once a landscape of traditional steelworks, the area is undergoing a rapid “hotspot-ification” (핫플화), becoming a trendy commercial and cultural destination that attracts new businesses and drives up property values. This organic gentrification is now being accelerated by a wave of formal redevelopment projects.
Key projects acting as catalysts include:
- Yeongdeungpo Downtown Station Area Urban Redevelopment: Union establishment has been approved.
- Yeongdeungpo Jjokbang-chon Public Housing Project: The business plan has received approval.
- Daesun Flour Mill Redevelopment (Areas 1 and 2): Large-scale redevelopment of a landmark industrial site.
- Mullae-dong 4-ga Redevelopment: The project contractor has been selected.
- Mullae-dong 1-ga, 2-ga, and 3-ga: Designated redevelopment zones where value is currently being driven by the “hotspot-ification” phenomenon, preceding formal large-scale development.
3.2 Guro: Large-Scale Distribution Hub Innovation
The investment opportunity in Guro is centered on the planned spatial innovation for its large-scale, yet aging, distribution facilities. The city’s plan targets major complexes, including the Guro Machine Tool Commercial Complex (구로기계공구상가), Guro Central Distribution Complex, and Siheung Distribution Complex, for modernization and redevelopment, signaling a future shift towards higher-value land use.
3.3 Regional Value Multiplier: Major Infrastructure Projects
Beyond zoning changes, Seoul is actively investing in placemaking infrastructure designed to fundamentally upgrade the corridor’s commercial and residential appeal, exemplified by the following projects:
Gukhoe-daero (National Assembly Boulevard) Undergrounding & Linear Park Project
This landmark project aims to dramatically improve the residential environment and unlock new commercial potential by relocating a major arterial highway underground. A large linear park will be created on the reclaimed land, drawing a direct parallel to the highly successful Gyeongui Line Forest Park.
- Timeline: Road facilities are scheduled for completion by 2029, with the park to be finished by 2030.
- Impacted Areas: The project will directly benefit properties in Yangcheon-gu and Gangseo-gu.
New Railway Network Expansion
Critical new railway lines are set to drastically reduce commute times and connect the Southwest Corridor to major employment hubs across the metropolitan area.
- Sinansan Line: An accident has caused an estimated 3-4 year delay for the main line, pushing its completion to approximately 2030.
- Daejang-Hongdae Line: This new line is vital for enhancing job accessibility from the Southwest Corridor to key business districts such as Yeongdeungpo, Yeouido, Magok, and Gangnam. With its plan approval expected in September 2025, construction is imminent, targeting a 2031 completion date.
As Seoul’s core undergoes this multifaceted regeneration, the investment landscape expands outward into the high-growth potential of the surrounding Gyeonggi Province.
4.0 High-Growth Frontier: Northern Gyeonggi Province (경기 북부)
Northern Gyeonggi is a region defined by rapid, large-scale development. Its growth is fueled by the systematic construction of new towns, the expansion of its industrial base, and the rollout of critical transportation links designed to improve connectivity with Seoul’s economic centers. This combination of residential and industrial expansion creates a compelling growth narrative.
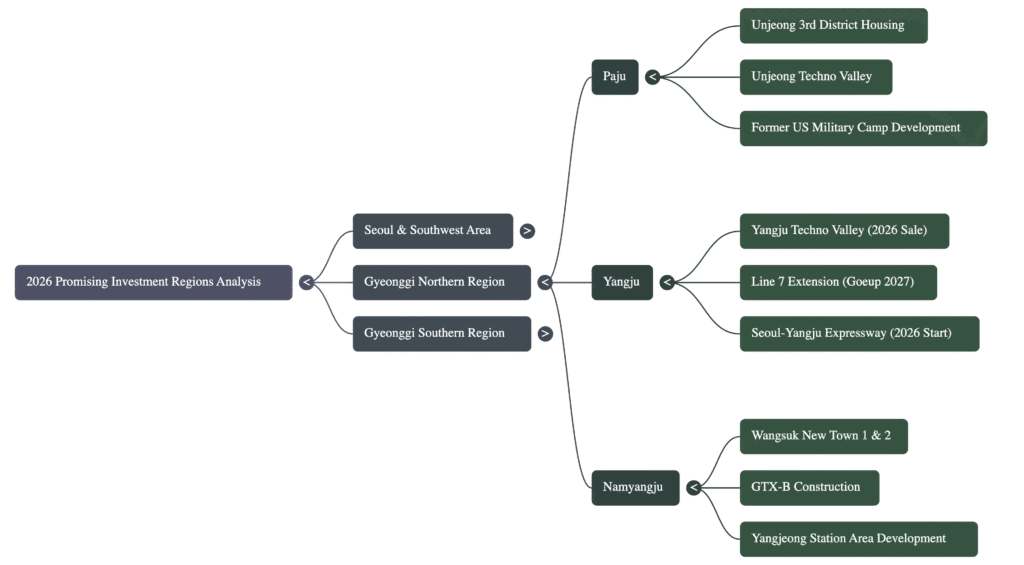
4.1 Paju City
Paju’s development is driven by a combination of new town settlement, industrial park planning, and the redevelopment of former US military installations.
- Unjeong New Town: The first two districts are fully occupied, with the third district undergoing sequential occupancy expected to continue until 2028.
- Unjeong Technovalley: The development model has been shifted from private to public sector-led, with a feasibility study currently underway and scheduled for completion in December 2025.
- Redevelopment of Returned US Military Bases: Several large former bases are being repurposed for urban and industrial use, with key milestones expected in 2026.
| Camp Name | Location (Dong/Ri) | Planned Use | Housing Units | Key 2026 Milestone |
| Camp Edwards | Wolong-myeon, Yeongtae-ri | Urban Development | ~7,000 | Business plan approval and official plan announcement scheduled |
| Camp Howes | Jori-eup, Bongilcheon-ri | Urban Development | 5,300 | Compensation scheduled to begin |
| Camp Giant | Munsan-eup, Seonyu-ri | Urban Development | ~6,500 | Business plan approval and official plan announcement scheduled |
| Camp Stanton | Gwangtan-myeon, Sinsan-ri | Industrial Park | N/A | Industrial park implementation plan approval scheduled |
- Infrastructure: The Gimpo-Paju section of the Capital Region’s 2nd Ring Expressway is 52% complete, with an expected opening in December 2027.
4.2 Goyang City
Goyang’s growth is concentrated in two distinct zones, one centered on business and culture in Ilsan and the other on new residential supply in Deogyang-gu.
- Ilsan Area: A major cluster of projects is materializing around the KINTEX exhibition center.
- Ilsan Technovalley: Currently 35% complete, with phased land sales commencing in October 2025 and a target completion date in the second half of 2027.
- K-Culture Valley (formerly CJ Live City): The Live Nation Consortium has been selected as the preferred bidder. Construction is targeted to start in May 2026, with completion by 2030.
- Transportation: A key milestone for the GTX-A line is the planned extension of its service from Seoul Station to Suseo in June 2026.
- Deogyang-gu Area: This area is anchored by large-scale housing projects and new transportation hubs.
- Changneung New Town: This massive project includes 38,000 households, with the first occupancy scheduled for December 2027. The new GTX-A Changneung Station is targeted to open in 2030.
- Daegok Station Area Development: District designation for this transit-oriented development is planned for 2026, with an occupancy target of 2031.
4.3 Gimpo City
Gimpo’s investment profile is defined by ambitious, large-scale urban and industrial development plans designed to accommodate significant population growth.
- Gimpo Hangang 2 District (Compact City): A major new town with 46,000 households planned. The district plan approval is expected in December 2026, with the first housing sales to begin in 2030.
- Pungmu Station Area Development: This 6,500-household project began site construction in November 2024. Apartment sales are set to commence in August 2025, with project completion by December 2027.
- Hangang Cinepolis Industrial Complex: This long-term project (2009-2026) will see apartment sales start in June 2025.
- Transportation: Gimpo’s connectivity is set for a major upgrade. The Western Capital Region Express Railway (서부권 광역급행철도), linked to the GTX-D line, passed its preliminary feasibility study in July 2025. A feasibility study for the Seoul Subway Line 5 extension is also ongoing.
4.4 Yangju & Namyangju Cities
These eastern cities are defined by massive new town developments supported by crucial new transit lines connecting them to Seoul.
- Yangju: Development is centered on two large new town districts, Okjeong (45,000 households) and Hoecheon (24,000 households), which are currently in phased occupancy. The Yangju Technovalley is scheduled for land sales in 2026, and construction on the Seoul-Yangju Expressway is planned to start in late 2026. The Line 7 extension and GTX-C line are the critical transit upgrades underpinning this growth.
- Namyangju: The city is home to the massive Wangsuk New Town project, which includes 52,000 households in District 1 and 15,000 in District 2, with occupancy planned from 2028. This growth is supported by two major rail projects: the GTX-B line (currently under construction, targeting a 2031 opening) and the Line 9 extension (targeting 2031, but currently facing delays).
We now pivot from the northern region’s residential and industrial expansion to the technology-centric growth corridor developing in the south.
5.0 The Economic Engine: Southern Gyeonggi Province (경기 남부)
Southern Gyeonggi Province stands as the undisputed core of South Korea’s high-tech economy, particularly the global semiconductor industry. Investment opportunities here are directly linked to the creation of mega-scale industrial clusters and the extensive transportation and residential infrastructure being developed to support this economic engine.
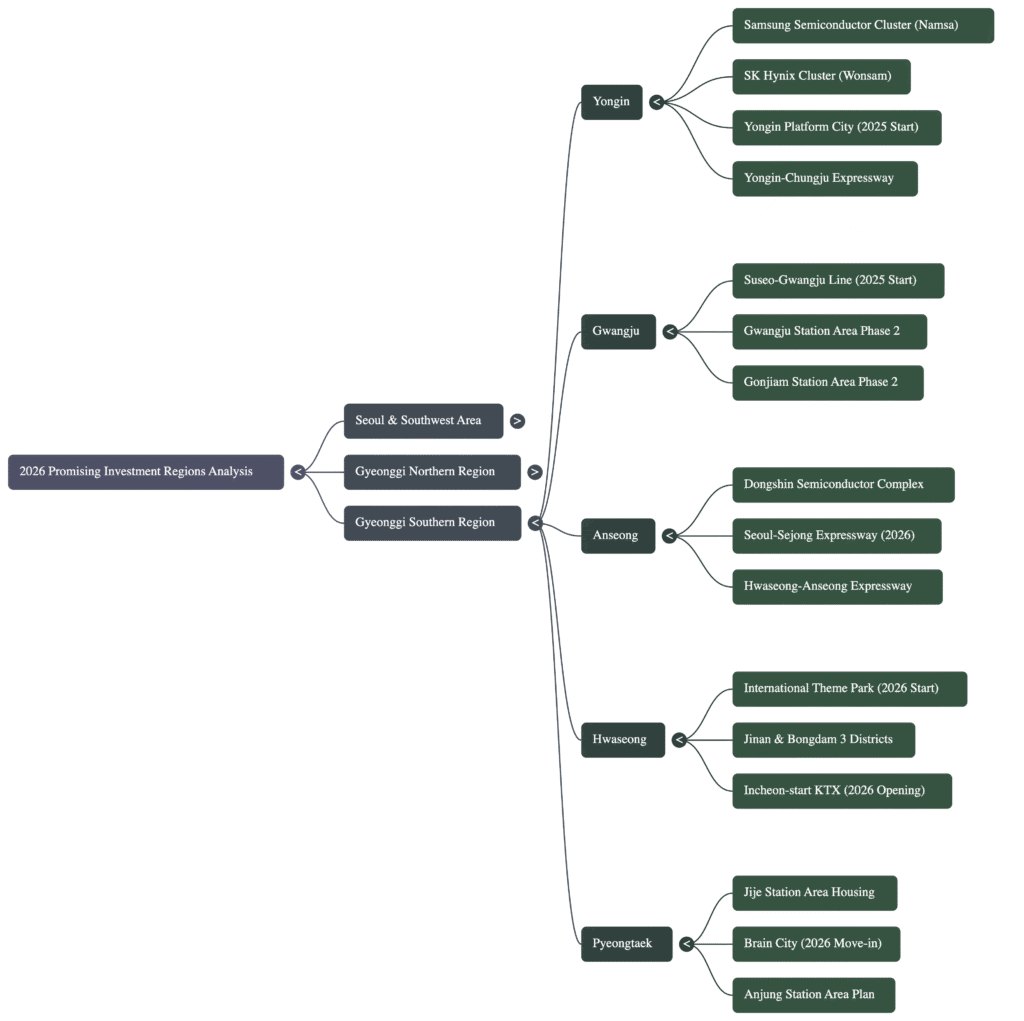
5.1 Gwangju City
Gwangju is set to benefit significantly from improved rail connectivity to Seoul’s Gangnam district. The Suseo-Gwangju rail line is slated to begin construction in late 2025 for a planned 2030 opening. This project is spurring several associated station-area developments with key milestones in 2026.
- Gwangju Station Area (Phase 2): Aims for district designation approval in the first half of 2026.
- Samdong Station Area: A development restriction notice was issued in November 2025, signaling the imminent start of formal planning.
- Gonjiam Station Area (Phase 2): The compensation plan announcement is scheduled for March 2026, with project completion aimed for late 2030.
5.2 Yongin City: The Global Semiconductor Hub
Yongin has emerged as the most critical investment location in the region, attracting hundreds of trillions of KRW in investment from the nation’s leading semiconductor companies. Two mega-projects form the core of this industrial expansion.
| Project Name | Lead Company | Investment Size | Key Features | 2026 Milestone |
| Yongin Advanced System Semiconductor Cluster National Industrial Complex | Samsung | 360 Trillion KRW | 2.35 million pyeong, 6 new fabs | Compensation for land acquisition begins |
| Yongin Semiconductor Cluster | SK Hynix | 122 Trillion KRW | 1.26 million pyeong, 4 new fabs,<br>1st fab under construction | 1st fab construction ongoing, road expansions<br>(e.g., National Route 57) near completion |
Supporting this industrial boom is the Yongin Platform City, a large-scale urban development project designed to provide housing and commercial amenities. It will feature 10,000 households, direct access to the GTX-A line at Guseong Station, and is scheduled for completion in 2030 after a March 2025 construction start.
5.3 Anseong City: A Strategic Beneficiary
Positioned along the expanding semiconductor belt, Anseong is a key strategic beneficiary of the growth in Yongin and Pyeongtaek.
- Dongsin Industrial Complex (Semiconductor Materials/Parts): After a previous rejection, a revised plan is being prepared for resubmission for provincial review in the second half of 2026.
- Anseong Technovalley: Most of the industrial land in this complex has been sold, with project completion expected in late 2026.
- Infrastructure: The Anseong-Sejong section of the Seoul-Sejong Expressway is a critical infrastructure link targeted for a late 2026 opening.
5.4 Hwaseong & Pyeongtaek: Diversified Growth and Logistics
Hwaseong and Pyeongtaek are mature industrial hubs that continue to see diversified, large-scale development in housing, entertainment, and logistics.
- Hwaseong International Theme Park: Construction is scheduled to begin in 2026, with a Phase 1 opening planned for 2030.
- Hwaseong Bongdam 3 District: This project for 18,000 households is slated to begin land compensation in late 2026.
- Hwaseong Jinan Public Housing District: A larger project for 34,000 households, with land compensation planned for late 2028.
- Pyeongtaek Jijeyeok Station Area: A massive 33,000-household development. The district plan is scheduled for submission in December 2025, with construction starting in 2027.
- Pyeongtaek Brain City: This 18,000-household project will see its first residents move in starting July 2026.
- Regional Rail: Two key rail links are set to open in 2026: the disconnected Seohwaseong-Wonsi section of the Seohae Line in March—a crucial link activating connectivity for Hwaseong and Pyeongtaek—and the Incheon-bound KTX service via Hwaseong’s Eocheon station in December.
Southern Gyeonggi offers a robust and diversified mix of investment opportunities, ranging from direct exposure to the high-tech industrial boom to large-scale residential and infrastructure development.
6.0 Conclusion and Strategic Outlook for 2026
The real estate investment landscape in the Seoul Metropolitan Area is being actively and profoundly shaped by three core pillars moving into 2026. First, Seoul’s urban regeneration policy is the foundational catalyst, providing a clear roadmap for unlocking value in historically underutilized industrial lands, with the Southwest Corridor as its first tangible proving ground. Second, the relentless expansion of the GTX and other high-speed rail networks into Gyeonggi Province is redefining commuter patterns and creating new residential growth frontiers. Third, the immense public and private investment flowing into the Southern Gyeonggi semiconductor belt is creating a world-class economic engine that fuels demand for industrial, commercial, and residential real estate across the entire region.
For investors, the most actionable opportunities are tied to clear, dated milestones. A strategic focus should be placed on locations with scheduled events in 2026 that will act as powerful catalysts for value appreciation. These include the official announcement of redevelopment plans, the commencement of land compensation for major public housing or industrial projects, and the opening of key transportation links. By aligning investment timelines with these tangible catalysts, investors can strategically position themselves to capitalize on the transformative growth of the Seoul Metropolitan Area.